The following topics provide an overview of TCAP and how it is used to provide enhanced network services:
- Generic service interface
- Role of TCAP in call control
- TCAP within the SS7 protocol stack
- Transaction and component sublayers
Generic Service Interface
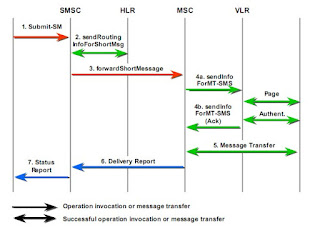
TCAP is designed to be generic to accommodate the needs of a wide variety of different services. Some common services that use TCAP include number translation services, such as Enhanced 800 Service and Local Number Portability (LNP). Other examples of TCAP users are Custom Local Area Signaling Services (CLASS), Mobile Wireless, and Advanced Intelligent Network (AIN) services. Figure below shows how TCAP uses standardized components as the basic building blocks for services across network nodes.
Most TCAP services can be viewed as a dialogue of questions and answers. A switch needs additional information that is associated with call processing, or with a particular service that causes it to send a TCAP query that requests the needed information. As shown in Figure below, the answer returns in a TCAP response, which provides the necessary information, and normal call processing or feature processing can resume. The query for information can be sent to a Service Control Point (SCP) or to another SSP, depending on the type of service and the information required. The SCP is an SS7-capable database that provides a centralized point of information retrieval. It typically handles number translation services, such as toll-free and LPN; however, SCPs are also used for a number of additional IN/AIN services.
Role of TCAP in Call Control
TCAP is used to provide information to SSPs. This information is often used to enable successful call completion, but TCAP is not involved in the actual call-setup procedures. This interaction between the service information provided by TCAP and the circuit-related protocol that performs the call setup occurs at the application level, not at the SS7 protocol layer.
TCAP Within the SS7 Protocol Stack
As shown in Figure below, TCAP is at level 4 of the SS7 protocol stack. It depends upon the SCCP's transport services because TCAP itself does not contain any transport information. First, SCCP must establish communication between services before TCAP data can be delivered to the application layer. Refer to Chapter 9, "Signaling Connection Control Part (SCCP)," for more information on SCCP's transport services. TCAP interfaces to the application layer protocols above it, such as the ITU Intelligent Network Application Part (INAP), ANSI AIN, and ANSI-41 Mobile Switching to provide service-related information in a generic format. The application layer that passes information down to be encapsulated within TCAP is known as a Transaction Capability User (TC-User). The terms application, service, and TC-User are used interchangeably.
Figure: TCAP Within the SS7 Stack